Contents
What is Ovarian Cancer?
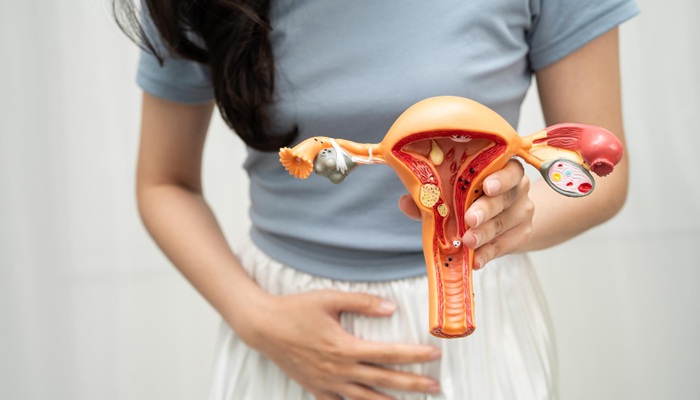
Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that occurs when abnormal cells in the ovaries or fallopian tubes grow and reproduce uncontrollably.
The ovaries are part of the female reproductive system. These walnut-sized, round organs produce eggs during a woman’s reproductive years.
Ovarian cancer is divided into several types, including:
- Epithelial ovarian cancer: This is the most common type and includes several subtypes, such as serous carcinoma and mucinous carcinoma.
- Stromal tumors: These rare tumors are usually diagnosed at an earlier stage compared to other types of ovarian cancer.
- Germ cell tumors: This rare type of ovarian cancer tends to occur in younger women.
Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer can develop and spread throughout the abdomen before causing any noticeable symptoms, making early detection difficult.
Some potential symptoms include:
- Abdominal bloating or swelling
- Feeling full quickly when eating
- Weight loss
- Discomfort in the pelvic area
- Fatigue
- Back pain
- Changes in bowel habits, such as constipation
- Frequent urination
Causes of Ovarian Cancer
The exact cause of ovarian cancer is not known. However, some people are at a slightly higher risk of developing it.
Risk factors for ovarian cancer include:
- Being over the age of 60
- Obesity
- A family history of ovarian cancer or inherited genetic mutations (BRCA1 or BRCA2) or Lynch syndrome
- Never having been pregnant or having children later in life
- Endometriosis
The risk also increases with age.
Diagnosis of Ovarian Cancer
If a doctor suspects ovarian cancer, they will ask about your symptoms and perform a pelvic examination. During this exam, the doctor checks for abnormal growths or enlarged organs.
Doctors may also recommend several tests to diagnose ovarian cancer:
1. Imaging tests
- Pelvic ultrasound
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
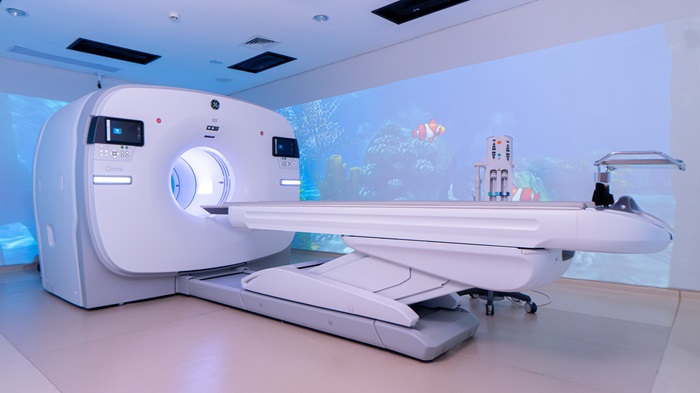
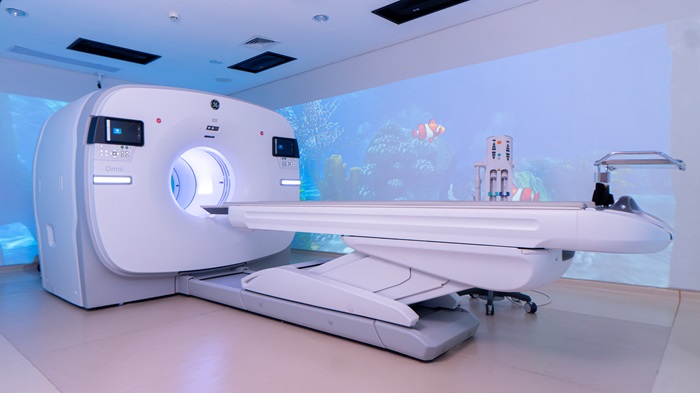
- CT scan (computed tomography)
- PET scan (positron emission tomography)
2. Blood tests
Blood tests are used to detect the presence of a substance called CA-125. High levels of CA-125 in the blood can be a sign of cancer. However, CA-125 levels can be normal even in people with cancer, and elevated levels may also occur in other medical conditions.
Therefore, doctors often use a combination of blood tests and other diagnostic methods.
3. Surgical evaluation
In some cases, doctors may diagnose ovarian cancer during surgery. If abnormal growths are found, they are typically removed during the same procedure.
4. Laparoscopy
During a laparoscopy, a thin camera (laparoscope) is inserted through a small incision in the abdomen.
Using the camera and additional instruments, the surgeon can assess the cancer, perform a biopsy, and remove ovarian tumors.
Treatment for Ovarian Cancer
-
Surgery
Ovarian cancer treatment through surgery typically involves removing the reproductive organs and any other affected areas. Doctors may use laparoscopy (minimally invasive surgery) or laparotomy (open surgery through a larger abdominal incision).
-
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy may be recommended before or after surgery. It involves drugs designed to target and kill cancer cells. It can be administered intravenously or orally.
-
Targeted therapy
This cancer treatment uses drugs that identify and attack cancer cells. It works by changing how the cancer cells grow and divide.
-
Hormone therapy
Some ovarian cancers grow in response to hormones. Hormone therapy can block these hormones, slowing or stopping the cancer’s growth.
-
Brachytherapy
Brachytherapy is a form of internal radiation therapy, meaning the radiation source is placed directly near the tumor inside the body. The radiation source is in the form of a very small capsule inserted into the body through a thin tube.
Do you have further questions or want to consult about cancer? Feel free to visit the Mandaya Comprehensive Cancer Center. Our hospital is equipped with modern technology to treat various types of cancer, supported by an experienced team of specialist doctors.
Schedule an appointment easily through the Chat feature on WhatsApp, Book Appointment, or the Care Dokter app, available on Google Play and the App Store to simplify your visit, view queue numbers, and access more detailed information.