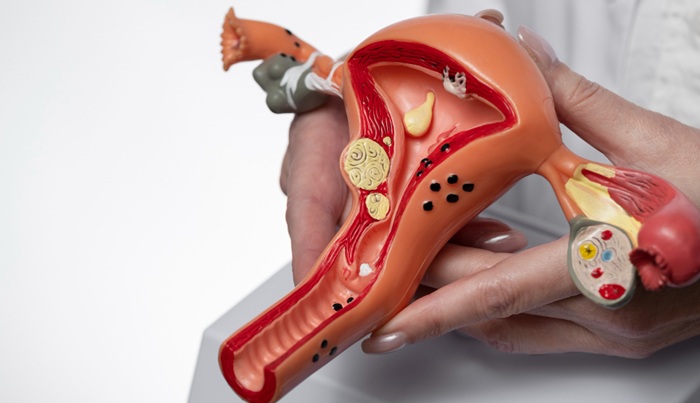
Uterine cancer is a type of cancer that affects the uterus, the organ where a baby grows and develops during pregnancy. Any woman of any age can develop uterine cancer. However, this condition most commonly occurs in women who have entered menopause or are over the age of 50.
What is Uterine Cancer?
Uterine cancer is the abnormal growth of cells in the uterine tissue. In most cases, cancer cells originate in the inner lining of the uterus, known as the endometrium. This lining is where a fertilized egg (ovum) attaches, which is why this condition is also known as endometrial cancer.
Apart from the endometrial lining, cancer cells can also grow in the connective tissue or muscle surrounding the uterus.
Types of Uterine Cancer
There are two main types of uterine cancer, classified based on the location where cancer cells develop:
- Endometrial Cancer
- This type of cancer begins in the endometrium and is one of the most common reproductive system cancers in women.
- Uterine Sarcoma
- This type of cancer originates in the middle muscle layer (myometrium) and connective tissue of the uterus. Uterine sarcoma is considered very rare.
Symptoms of Uterine Cancer
Common symptoms of uterine cancer may include:
- Vaginal bleeding outside of the menstrual cycle or after menopause
- Heavier or longer menstrual periods than usual
- Unusual vaginal discharge with a foul odor
- Pain in the lower back or pelvis
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Blood in the urine
- Lump or swelling in the abdominal or pelvic area
However, these symptoms may also resemble signs of other conditions. To determine the cause of your symptoms, consult a doctor for further evaluation.
Causes of Uterine Cancer
Uterine cancer is caused by genetic mutations in the cells of the uterine tissue. These mutations cause cells in the uterus to divide uncontrollably, crowding out healthy cells.
Although the exact cause of these mutations is unknown, several factors may increase the risk of developing uterine cancer, including:
- Age over 50
- Menopause
- Overweight or obesity
- High-fat animal diet
- Family history of uterine cancer
- Inherited Lynch syndrome
- High estrogen levels
- Diabetes
- Endometriosis
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Hormone replacement therapy with estrogen or tamoxifen
- Early menstruation (before age 12)
- Late menopause
Diagnosis
A doctor will begin diagnosing uterine cancer by evaluating your medical history, symptoms, risk factors, and family history. A physical and pelvic examination will also be performed.
Several tests may be conducted to confirm a diagnosis of uterine cancer, including:
- Blood tests
- Imaging tests such as CT scans, MRI, or transvaginal ultrasound
- Endometrial biopsy
- Hysteroscopy
- Dilation and curettage (D&C)
These tests not only help determine whether you have uterine cancer but also assist in developing an appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment for Uterine Cancer
Treatment for uterine cancer depends on the type and stage of the cancer, as well as your overall health condition. Common treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and hormone therapy.
Often, a combination of two or more treatment methods is used. The following are some treatment options for uterine cancer:
- Surgery
Surgery is generally the primary treatment for endometrial cancer. Some surgical options include:- Hysterectomy
- A procedure to remove the uterus and cervix, performed through an abdominal incision or vaginally.
- Depending on the cancer stage, the doctor may remove only the uterus if the cancer has not spread. If it has spread, the uterus, cervix, and surrounding tissues may be removed.
- Bilateral Salpingo-Oophorectomy (BSO)
- A procedure to remove the uterus along with the ovaries and fallopian tubes, often necessary to ensure all cancer cells are eliminated.
- Lymphadenectomy
- A procedure to remove the uterus along with lymph nodes around the uterus to check for cancer spread.
- Hysterectomy
- Chemotherapy
- A treatment using chemical compounds to destroy cancer cells. Chemotherapy can be administered orally, by injection, or via implantable devices.
- Radiotherapy
- Uses high-energy radiation to destroy cancer cells. This treatment can kill cancer cells or stop them from growing.
- One commonly recommended radiotherapy method for uterine cancer is brachytherapy.
- Hormone Therapy
- A treatment that involves administering or blocking certain hormones to combat cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy
- A treatment that strengthens the immune system to help fight cancer.
Prevention of Uterine Cancer
While there is no vaccine or medication to prevent uterine cancer, certain steps can help reduce the risk:
- Consult a doctor if you have multiple risk factors for uterine cancer.
- Maintain a healthy weight by eating a nutritious diet and exercising regularly.
- Manage diabetes effectively.
- Have regular reproductive health check-ups.
- Use hormonal birth control as directed by a doctor.
Uterine cancer is often detected in its early stages because many women seek medical attention upon experiencing abnormal vaginal bleeding.
Consult an Expert
To determine how often you need check-ups or which tests are appropriate, consult an obstetrician-gynecologist (OBGYN) or an oncology surgeon.
You can visit the Advanced Cancer and Radiotherapy Centre at Mandaya Royal Hospital Group to consult with our experts. Schedule an appointment via WhatsApp chat, Book Appointment, or the Care Dokter app, available for download on Google Play and the App Store. This will facilitate your visit, allow you to check queue numbers, and access other complete information.
The treatment of uterine cancer at Mandaya Royal Hospital Puri is managed by a multidisciplinary team of highly skilled specialists, including:
1. Obstetrics and Gynecology Specialist with a Subspecialty in Oncology
a. Dr. dr. Unedo Hence Markus Sihombing, Sp.OG, Subsp. Onk


b. dr. Kartika Hapsari, Sp.OG, Subsp.Onk, FNVOG


2. Radiation Oncology Specialist
a. Prof. Dr. dr. Soehartati A. Gondhowiardjo, Sp.Onk.Rad (K)

b. dr. Riyan Apriantoni, Sp.Onk.Rad

c. dr. Novina Fortunata, Sp.Onk.Rad


3. Internal Medicine Specialist with a Consultant in Hematology and Medical Oncology
a. Prof. DR. Aru W. Sudoyo, Sp.PD-KHOM, FINASIM, FACP


b. dr. Alvin Tagor Harahap, Sp.PD-KHOM

c. dr. Toman T.J Lumban Toruan, Sp.PD-KHOM


4. Surgical Specialist with a Subspecialty in Oncology
a. dr. Abdul Rachman, Sp.B (K) Onk


b. dr. Enos H. Siburian, Sp.B (K) Onk