The heart has its own electrical system that helps it beat. If the heart’s electrical system is disrupted, the heart may beat irregularly, either too fast or too slow. If the heart’s electrical activity is not stabilized, it can lead to heart failure, and in the most dangerous cases, it can cause death.
Some symptoms that may occur when the heart’s electrical system has issues include palpitations, dizziness or lightheadedness, fainting, fatigue, reduced endurance, shortness of breath, and chest pain. Cases of weak or problematic heart electrical activity can be treated by a cardiologist specializing in arrhythmia.
For arrhythmias where the heart beats too fast, dr. Sebastian Andi Manurung, Sp.JP (K), a Cardiologist and Arrhythmia Specialist, will use the heart ablation method, which involves neutralizing the excess electrical generator in the heart.
How Does The Heart Ablation Process Work?
First, the doctor will map the heart’s electrical system using a mapping system to determine the location of the electrical disturbance. This mapping procedure only requires local anesthesia in the thigh area. The doctor will perform a catheterization procedure by inserting a catheter/infusion tube through the thigh, which then leads to the heart.
Using PentaRay NAV Mapping technology, the doctor can see the heart’s anatomical mapping on the screen and locate the spot where the electrical disturbance is occurring, marked in red. Once the location is identified, the doctor will proceed with the heart ablation process, which neutralizes the excess electrical generator while monitoring the heart rate in real-time.
If the disruptive electrical source is neutralized, it will immediately be visible on the heart’s ECG recording in the catheterization room, showing a return to normal. No medical devices are left inside the body during the heart ablation procedure; all tubes, ablation devices, etc., are removed. After the ablation procedure, the patient will be hospitalized for approximately two days for recovery.

EKG results on the cathlab screen
What About Arrhythmias Where The Heart Beats too Slowly?
This type of arrhythmia is called bradycardia. It is caused by the aging process, which can lead to a decline in the function of the heart’s electrical generator. Therefore, we need to add a battery or electrical generator to the heart, known as a pacemaker.
The process of installing a pacemaker only requires local anesthesia in the heart catheterization room. The heart battery is implanted under the skin in the chest, below the collarbone, and connected to the heart’s natural wiring. The lifespan of a pacemaker typically ranges from 8 to 10 years, and regular check-ups should be done every six months.
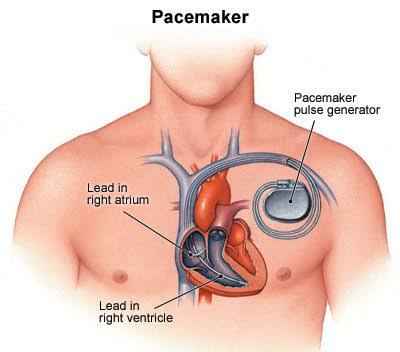
Pacemaker placement location
For consultation regarding heart problems at the Heart Center of Mandaya Royal Hospital Puri, you can use the Chat via WhatsApp feature, Book Appointment, or the Care Doctor application, which can be downloaded on Google Play and the App Store, to facilitate visits, check queue numbers, and obtain complete information.