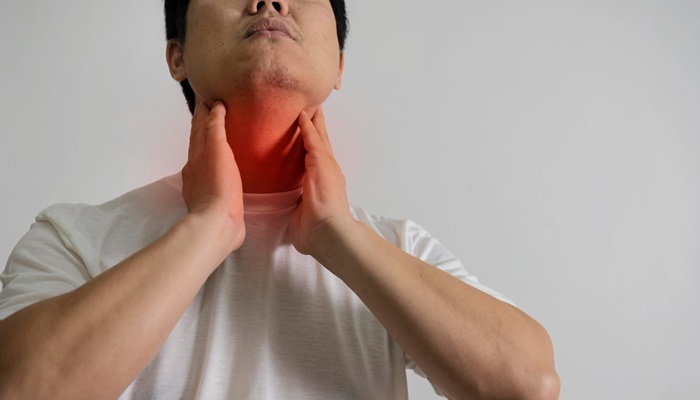
Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones, namely triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). These hormones play a crucial role in regulating metabolism. When thyroid hormone production decreases, various bodily functions slow down, leading to multiple symptoms and health complications.
This thyroid disorder often goes undetected until complications arise. Some of these complications include mental health issues, breathing difficulties, abnormal body temperature, heart problems, and goiter (thyroid gland enlargement).
Contents
Causes of Hypothyroidism
Several common causes of hypothyroidism include:
- Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
This autoimmune disease is the most common cause of hypothyroidism, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland. - Hyperthyroidism Treatment
Treatments for hyperthyroidism, such as radioactive iodine therapy or surgery, may lead to decreased thyroid hormone production. - Iodine Deficiency
Iodine is essential for thyroid hormone production. A lack of iodine intake can result in hypothyroidism. - Congenital Disorders
Some people are born without a thyroid gland or with an underdeveloped thyroid gland, leading to low hormone production. - Medications and Radiation Therapy
Certain medications and radiation therapy can interfere with thyroid function. - Thyroid Surgery
Partial or complete removal of the thyroid gland may cause hypothyroidism.
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
The symptoms of this condition vary depending on the severity of hormone deficiency. Common symptoms include:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Unexplained weight gain
- Dry skin and hair loss
- Sensitivity to cold
- Constipation
- Depression and mood disorders
- Swelling in the face and neck (goiter)
- Slow heart rate
- Muscle and joint pain
- Irregular or heavy menstrual cycles in women
Diagnosis of Hypothyroidism
To diagnose hypothyroidism, doctors typically conduct several tests, including:
- Physical Examination: Checking for physical signs such as neck swelling and changes in skin and hair.
- Blood Tests: Measuring levels of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). High TSH and low T4 levels indicate hypothyroidism.
Treatment for Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is typically treated with thyroid hormone replacement therapy. Common treatments include:
- Levothyroxine Medication: This synthetic thyroid hormone helps restore normal hormone levels.
- Regular Monitoring: Routine blood tests are necessary to monitor thyroid hormone levels and adjust medication dosage if needed.
- Lifestyle Changes: Maintaining a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle can support treatment and help manage symptoms.
See also: No Need to Go Abroad, at Mandaya Royal Hospital Puri Hyperthyroidism Can Be Cured Without Surgery
Preventing Hypothyroidism
Some preventive measures to reduce the risk of hypothyroidism include:
- Ensuring Adequate Iodine Intake: Consuming iodized salt and iodine-rich foods such as seafood, dairy products, and eggs.
- Regular Health Check-ups: Periodic thyroid examinations, especially if there is a family history of thyroid disorders.
- Avoiding Radiation Exposure: Minimizing exposure to high radiation levels that may damage the thyroid gland.
- Managing Autoimmune Diseases: If you have another autoimmune condition, maintaining optimal health may help prevent hypothyroidism.
When to See a Doctor?
If you experience any concerning symptoms, consult a doctor immediately for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
For expert thyroid care, visit Mandaya Hospital. Our Indonesian Thyroid Center provides top-quality services for various thyroid conditions. Supported by experienced specialists and advanced medical equipment, we offer treatments ranging from medication to thyroid ablation procedures.
See also: Hyperthyroidism Can Be Cured at Mandaya Royal Hospital Puri Without Drug Dependence
Schedule a consultation via WhatsApp Chat, Book Appointment, or through the Care Dokter app, available on Google Play and the App Store.