What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
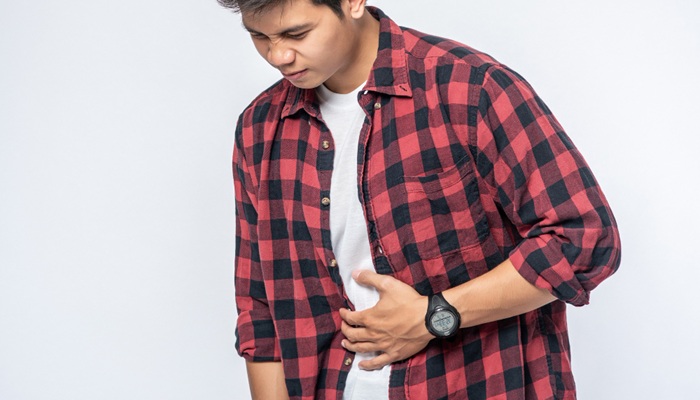
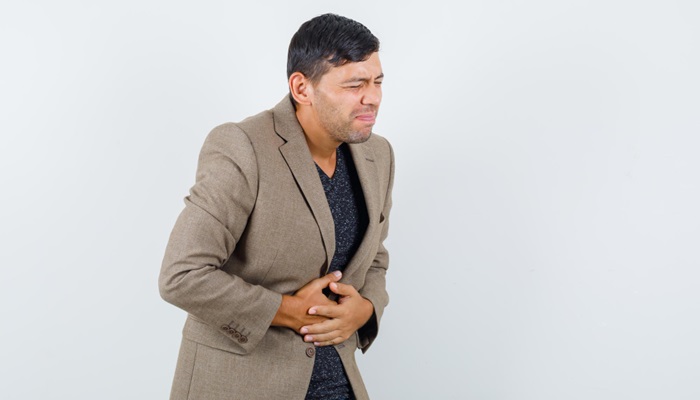
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes pain, swelling, and stiffness in the lining of the joints (synovium). This condition most commonly affects the joints in the fingers, hands, wrists, knees, ankles, feet, and toes. RA usually affects the same joints on both sides of the body.
In addition to joint symptoms, RA can sometimes affect other parts of the body, such as:
- Skin
- Eyes
- Mouth
- Lungs
- Heart
Stages of Rheumatoid Arthritis:
RA progresses in stages, which include:
Stage 1: In the early stage of RA, inflammation occurs in the joint tissue. Patients may feel joint pain and stiffness. X-rays usually do not show bone damage at this stage.
Stage 2: Inflammation begins to damage the cartilage in the joints. Patients may experience stiffness and reduced range of motion.
Stage 3: Inflammation becomes severe and damages the bones. Symptoms include increased pain, more stiffness, and a greater loss of mobility. Physical changes may become visible.
Stage 4: At this stage, active inflammation may subside, but joint function continues to deteriorate. Patients often experience intense pain, swelling, stiffness, and significant loss of mobility.
Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Common signs and symptoms of RA typically affect the wrists, hands, and feet, and include:
- Pain, swelling, and stiffness in more than one joint
- Low-grade fever
- Loss of appetite
- Unintentional weight loss
- Fatigue
- Dry eyes
- Chest pain
Causes of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Several potential causes and risk factors for RA include:
- Genetic factors: There is some evidence that RA can run in families, though the hereditary risk is considered low since genetics play a minor role.
- Hormonal factors: RA is more common in women, possibly due to the effects of estrogen. However, the connection is not yet proven.
- Smoking: Studies suggest that smoking may increase the risk of developing RA.
How Is Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing RA in its early stages can be difficult, as its symptoms can mimic other conditions like lupus or psoriatic arthritis.
If you experience symptoms of RA, it’s recommended to see a doctor within six months of symptom onset for early diagnosis and timely treatment.
Doctors will look for clinical signs of inflammation and ask about the duration and severity of symptoms. A physical exam will be conducted to check for swelling, functional limitations, and other signs.
Tests used to diagnose RA may include:
1. Blood Tests:
- Anti-CCP (anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies)
- Rheumatoid factor (RF)
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR or sed rate)
- C-reactive protein (CRP)
2. Imaging Tests:
- X-rays or MRI scans can help identify the type of arthritis and track disease progression over time.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment Options
Early treatment with specific medications can significantly improve long-term outcomes for RA. Often, a combination of medications is more effective than a single-drug approach.
Treatment options aim to relieve joint pain, reduce swelling and inflammation, and prevent or slow disease progression. Common medications for RA include:
- Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs)
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
- Corticosteroids
- Janus Kinase (JAK) Inhibitors
- Biologic Agents
Comprehensive Arthritis Care at Mandaya Royal Hospital Puri
Visit the Orthopedic & Movement Center at Mandaya Royal Hospital Puri for a complete evaluation, from early screening to advanced rheumatoid arthritis treatment.
Schedule an appointment easily via WhatsApp Chat, the Book Appointment feature, or the Care Dokter app, available on Google Play and the App Store. These tools help simplify your visit, check queue numbers, and access full information about your care.